Swollen eyelid is also known as puffy eye lid and is quite common condition that most of us come across sometimes in our lives.
This symptom could be mild or severe and can happen for some days to even months. Most of the times, swollen eye lid appears all of sudden, but in other cases, gradual inflammation is noticed. In either case, this should never be taken lightly.
What exactly is swollen or puffy eyelid?
A swollen eye lid is an inflammation of the eyelid that may or may not be due to excess fluid accumulation (edema) in connective tissues that surround the eye. Generally, puffy eye lid is not painful, and it can affect both upper and lower eyelids. Furthermore, it can affect to one or both eyes.
Causes of Swollen Eyelid
The general cause of swollen eyelid is retention of body fluid in the eyelid. This is seen during long hours of sleep or rest in the supine position. Other common causes of puffiness of eyelid are mentioned below:-
- Seasonal allergies
- High blood pressure
- Dermatitis (due to infection)
- Irritation to the eyelid due to chemicals
- Irritation due to makeup or cosmetic products
- Irritation due to contact lenses or lens solution
- Transferred allergen (as in touching eyelids by hands)
- Any trauma or malignancy
- Blepharitis (inflammation of eye margin)
- Pink eye or conjunctivitis (infection of eye)
- Cellulitis (it is of two types – preseptal cellulitis and orbital cellulitis)
- Herpes infection (eye herpes wherein the cornea is affected, and it is inflamed)
Depending upon the cause, the symptom of eyelid swelling may last long or subside within a few hours or days. For instance, if swollen eyelid is due to allergy from animal dander or dust particle, it may subside easily with some basic medication.
Swelling in the eyelid that has happened over the period of time could be due to some serious condition such as Graves Disease (hyperthyroidism) and require a particular care.
The commonest cause of swollen eyelid is eye allergy. Allergic condition of the eyelid can cause severe discomfort and the sufferer face a lot of difficulties in performing day to day tasks. Responding to allergens, the body’s immune system overreacts and releases histamines to fight allergens that have entered in the eye.
Along with histamines, some other chemicals are released that cause eye’s blood vessels to swell and become red. As a result of this response, the eyelid becomes red, itchy and secrets fluid continuously.
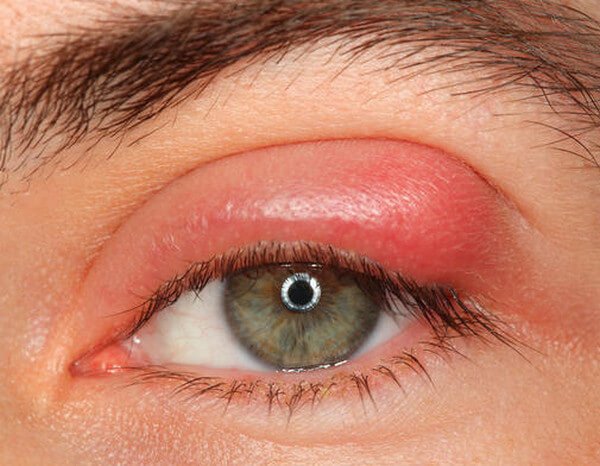
Conjunctivitis, Stye and Chalazion
Conjunctivitis and stye are common problems due to which eyelid inflammation may happen. A stye is caused due to bacterial infection that target oil producing glands in the eyelids. The condition of stye is painful and sometimes itchy. It appears like a reddish bump on the eye lid. If left untreated, it may get filled with a little pus. Styed eye is sensitive to the light is watery all the time.
A chalazion is caused when the oil producing glands are blocked. The glands then swell and further become a hard lump that results in reddening of the eyelid and inflammation.
Symptoms of Swollen Eyelid
- Redness of the affected eyelid
- Itching (in some cases) in the eye
- Watering from the affected eye
- Sticky discharge from the affected eye
- Irritation in the eye
- Pain in the eye (not always)
- Sneezing, malaise, headache (if swollen eye lid is associated with allergy)
Below mentioned are the symptoms require immediate medical attention if associated with swollen eyelid.
- Fever
- Vision disturbance (blurred vision, for instance)
- Uncontrolled eye movements
- Loss of eye movements or loss of control over eyelids
- Bulging or protrusion of the affected eye
- Any sign of anaphylactic shock such as swollen tongue/throat
- Breathlessness (dyspnea)
- Bleeding from the affected eye
- Giddiness
Differential Diagnosis of Swollen Eyelid
The differential diagnosis of edema and eyelid erythema is very broad. It ranges from benign, self-healing dermatoses to malignant tumors and vision threatening conditions. The best way is to examine the condition locally. The eyelid is examined, and symptoms are compared. Swollen red eyelids generally indicate cellulitis.
Orbital cellulitis is a serious infection observed with proptosis and ophthalmoplegia. The patient is to be shifted to the hospital, and intravenous broad spectrum antibiotics are administered to protect the vision.
Contact dermatitis, blepharitis and atopic dermatitis are quite common factors that cause edema and erythema and are less severe. Topical corticosteroids and good eyelid hygiene can help cure this.
Herpes infection in the eye is represented with vesicles, crusting or erosion. While malignant growth requires surgery, self-limiting benign eyelid nodular conditions such as chalaia and hordeola respond to warm compresses.
In all cases of eyelid swelling, along with physical examination lab tests are advised. Routine and micro examination of urine are carried out in case the physician suspects any kidney disease as the underlying cause of swollen eyelid. Blood report is helpful to diagnose whether swollen eyelid is due to bacterial or viral infection. Vision test is advised to ensure that the eyesight is intact.
Treatment of Swollen Eyelid
The swelling of eyelids (blepharitis) can be prevented and cured by maintaining proper hygiene. Follow below mentioned steps as remedies.
- Take a clean cloth and dip it in warm water. Squeeze the cloth and place it over eyelids for approximately 7 minutes. Repeat the process to keep the same temperature. ‘This helps in softening the crusts and loosens the oily portion.
- You may use baby shampoo (tearless) to wash the eyelids. Do this process gently using the index finger.
- Rinse the eyes thoroughly with clean water. Pat dry.
- In case of swollen eye lid due to particular microorganism, antibiotic is useful.
Prevention of Swollen Eyelid
The condition can be prevented by below mentioned steps:
- Maintaining proper hygiene (keep your hands and face cleaned and dust free)
- Keeping off your hands and avoiding rubbing of eyes
- Taking off the makeup from the eyes and face
Consult Your Doctor Immediately
You must contact your doctor immediately in case of profuse bleeding from eyelids. Also, in case of severe pus or septic and vision loss, emergency medical treatment from professional (ophthalmologist) is sought.
References
http://www.localhealth.com/
http://vision.about.com/od/
The Handbook of Ocular Disease Management by Sowka, Joseph W., Andrew S Gurwood and Alan G Kabat.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
http://www.webmd.com/eye-
