Swollen Uvula
Definition : Swollen Uvula (Uvulitis)
The uvula is an extension of soft palate and is small-elongated portion hanging structure in the back of the throat.
It is made up of highly vascular soft connective tissues surrounded by an epithelial layer. Swollen uvula, in medical term, is referred to as uvulitis. The function of this organ includes trapping microorganisms, prevent them to go into digestive tract and thus, keeping most of the illnesses at bay.
It is for this reason, this tiny organ is not advisable to remove unless severely affected or infected (as in cancer). The inflammation of uvula can happen due to many reasons but the condition is not so commonly seen. The condition occurs on both adults and children.
What Causes Swollen Uvula?
The inflammation of uvula (referred to as uvulitis) occurs mainly due to infection (mainly streptococcus of influenzae) or trauma. In children with fever, if the structure is severely inflamed, it is diagnosed as acute uvulitis (Source: Wald ER. Uvulitis. In: Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, 6th, Feigin RD, Cherry JD, Demmler-Harrison, GJ, Kaplan SL (Eds), Saunders, Philadelphia 2009. p.176.). The infection in uvula could be due to pharyngitis. Nevertheless, it is very unlikely to consider infectious uvulitis as the only source of infection.
The common cause of swollen uvula is dryness. A dry throat because of dehydration or sleeping with opened mouth can cause uvula to get infected and swollen. Let us have the summary of swollen uvula causes:-
- Dryness of throat
- Hot foods and beverages that burn the uvula and cause swelling
- Infection (mostly bacteria or virus)
- Alcohol abuse (in some cases)
- Any trauma to the throat
- Mouth ulcers
- Other respiratory tract infections
Signs and Symptoms of Swollen Uvula
In mild cases of uvulitis, the symptoms are bearable. Here is the list of uvulitis signs:
- Reddened structure of uvula
- Swelling on uvula and surrounding structure
- Fever
- Snoring
In severe condition of Uvulitis, following symptoms are reported:
- Difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia)
- Chokeing
- Difficulty in speaking
- Salivation
- Sleep apnea
- Nasal regurgitation
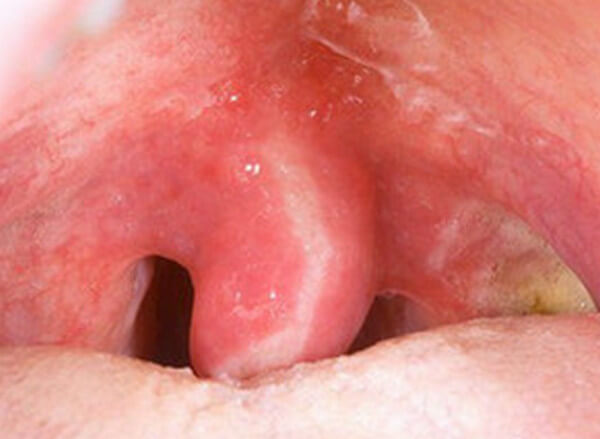
Diagnosing Swollen Uvula
The local examination is the primary tool to diagnose this condition. Nevertheless, here is the list of other techniques to diagnose this health ailment.
Blood test:
Hemogram (blood test) is advised to check the infection. Increase in white blood cells (WBC) may suggest the severity of the infection.
Culture:
The throat or uvula culture is carried out to see the exact cause. This helps decide which type of microorganism is responsible for uvulitis. A cotton swab is rubbed onto the structure and this is examined in the lab to identity the germ.
X-ray:
In some cases, the medical expert may advise to do X-ray especially when the case is severe and the victim is having severe problem in swallowing and complains of chokeing. X-ray of neck helps in diagnosing.
Clinical Presentation
Patients with swollen uvula are presented with sore throat, dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing) and the feeling of something in the throat. The patient may or may not have fever and has tendency to gag, spit or choke as they have severe discomfort while engulfing their own saliva.
Differential Diagnosis : Uvulitis and Epiglottitis
Epiglottis requires immediate attention and thus should be identified earliest. Epiglottitis could be life threatening disease because in this condition the windpipe becomes affected and the airway is blocked. The breathing becomes difficult and the death may happen due to respiratory failure.
The condition of epiglottitis is common in children (between the ages 2-6). Thus, children with fever and inflamed buckle cavity should require immediate medical attention by a pediatrician.
Treating swollen uvula
Antibiotics and antimicrobial:
The treatment of uvulitis depends upon its cause. Most of the bacterial infections are treated using broad-spectrum antibiotics. The medicines will help kill the microorganisms.
Steroids:
In some cases, medical experts do prescribe steroids to treat the swelling of uvula. This is quite commonly seen in case where uvulitis is because of allergic condition. Steroids help reducing inflammation, redness and pain.
Anti-allergic pills:
Antihistamines are common to prescribe tackling the condition of swelling uvula. These pills help in reducing the redness and itching.
Surgical Removal of Uvula
As mentioned before, surgical removal of uvula is done in extreme cases such as cancer. After surgery, the patient has to have utmost care to prevent infection and recurrence of the condition. The patient must follow the advises and regimen as instructed by the surgeon.
Natural and Home Remedies
Though natural remedies cannot considered as primary treatment for this condition, herbal remedies do help in alleviating the symptoms. However, one must understand that most of the home remedies give temporary relief and hence should not be considered as permanent cure. It is always better to contact your personal (family) healthcare provider before opting for any remedy for swollen uvula.
Gargling:
Warm salt-water gargling helps in reducing swelling. Gargle it after eating some ice for better results.
Ice:
Chewing some ice cubes help in reducing the swelling and thus may relieve the symptom of uvulitis.
Herbs:
Herbs like turmeric, ginger contain natural property of anti-inflammation. The decoction of raw turmeric and ginger is one of the most effective homemade remedies to help cure swollen uvula.
Honey:
Honey is another good kitchen remedy for swollen uvula. A teaspoon of honey licked twice a day to get rid of uvulitis. Herbalists also prefer this because honey help in neutralizing toxicity.
The intensity of symptoms of uvulitis can be lessened using eucalyptus cough drops.
If you have some herbal lozenges or throat spray, this can be used to reduce the symptoms of swollen uvula.
Herbal tea made up of ginger, holy basil leaves, cloves and black pepper help reducing the swelling and alleviate the symptoms of uvulitis.
If swollen uvula is due to dehydration, supplying the body with electrolytes. It helps treating this condition. Drink plenty of water and take juicy fruits and vegetables regularly as a must-have part of your meals.
Irritation and pain can be reduced taking some natural herbs (such as licorice and neem –Indian Margosa tree leaves) that have anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial effects.
When to see a doctor immediately
Though in most of the cases swollen uvula does not require immediate medical attention, there are some signs that you must consider seriously.
- Severe pain in uvula
- Severe difficulty in swallowing
- Difficulty in breathing
- Uneasiness due to lack of oxygen
- Choking and grunting
- Blood or pus from uvula (rupture)
References:
- Drugs.com
- Swollen uvula
- WebMD.com
- About.com
- Pediatric Infec Dis 1983;2:392-393
- Am J Emerg Med 1994; 1997
- Reference.com
- GroundReport.com
- Wikipedia
- Greenberg’s Text –Atlas of Emergency Medicine
- Ask.com community
Published by Dr. Raj MD under Diseases and Conditions.
Article was last reviewed on August 6th, 2018.

