Appendix Pain
What is Appendix and Appendicitis?
Appendicitis is an emergency condition which is characterized by the inflammation of the appendix.
Appendix is a finger-like pouch that is connected to the large intestine. It is located at the lower right abdominal quadrant [1]. Usually, it is 4 inches (10 cm) in length and pencil-thin [2]. This part of the body has no known function [3].
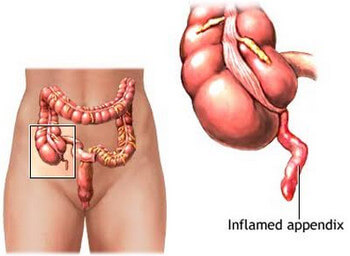
Picture 1: Picture of an inflamed appendix
Source: healthcentral.com
Anyone can be affected by this condition. Most of the time, people aged between 10 to 30 years old are affected [4]. Also, 1 out of 15 people can develop this medical disorder. It appears more in men than women [2].
Appendix Pain Location
Pain has been mentioned as the key in determining the presence of appendicitis. In the hospital, the most important question asked to a patient suspected with this condition is the location of the pain [3]. The location of the pain that is experienced in appendicitis has the following characteristics:
- Usually, appendix pain begins at the middle of the abdomen and near the navel. This occurs due to the appendix’ innervation that enters the spinal cord which is at the similar level of the navel (umbilicus).
- At the later stages, the appendix as well as the proximal or near abdominal wall gets irritated and swollen. This results in the localization of appendix pain at the right lower quadrant, with the exception in the children who are below three years of age.
- The appendix pain location can be determined with the use of various signs through the performance of assessment. First, when the physician touches the abdomen lightly or gently, the specific area will feel tender. Then, when the gentle pressure is released, the tenderness at the specific area will get worse. This symptom is also known as “Rebound Tenderness” or “Rebound Pressure”. It is actually what most physicians look for the confirmation of the condition’s diagnosis.
- Pain location may also be determined when a specific abdominal part hurts when the patient coughs, sneezes, moves around, or takes a deep breath. This location where appendix pain is found is also known as the McBurney’s Point. McBurney’s Point refers to the point located at the right abdominal side which is measured to be 1/3 of the anterior superior iliac spine’s distance to umbilicus.
- The appendix pain nature and location may vary such as in the cases of pediatric patients and pregnant women. [3, 5]
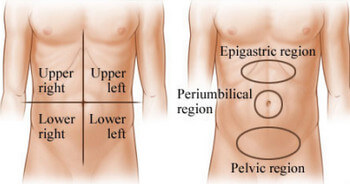
Picture 2: Abdominal Quadrants
Source: gastrohealthny.com
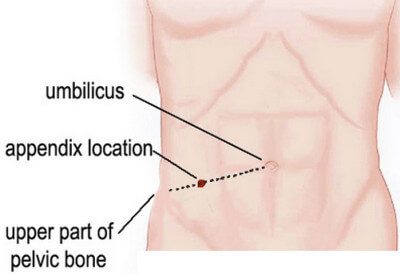
Picture 3: Appendix Pain Location
Source: healthhype.com
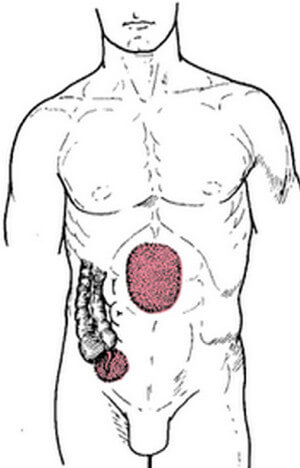
Picture 4: Areas affected by appendicitis
Source: medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com

Picture 5: McBurney’s Point Illustration
Source: thatgirlwiththescalpel.blogspot.com
Appendix Pain and Associated Symptoms
1. Abdominal Pain
- The main symptom of appendicitis. It usually develops immediately about for an hour.
- The pain felt in this condition starts at the mid-abdominal area near to the umbilicus. As it progresses, it becomes more localized to right lower portion of the abdomen. Worsening of appendix pain happens over the period of 6 to 24 hours.
- Rebound Tenderness: Pain that becomes more severe when the gentle pressure applied on the right lower abdomen is released.
- The quality of pain begins as dull and shifts to sharp type.
- Intensifies upon movement, coughing, sneezing, or deep-breathing
- In other cases, the pain may be noticed initially at the right lower abdominal quadrant.
2. Other symptoms
- Low-grade fever (37°C to 39°C)
- Appetite loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- Inability to pass gas, constipation or diarrhea
- Swelling and rigidity of the abdomen
- Frequent urination: This is associated to the irritation of the ureter’s lining (tube connecting the kidney and bladder) which is nearby the appendix area.
- Fever, malaise [2, 4, 6]
Causes of Appendix Pain
The main reason why appendix occurs is still unknown. According to medical experts, it can be caused by two factors:
1. Obstruction
- Appendix is a structure that is attached to the large intestines where stool formation occurs.
- There are appendicitis cases which are believed to result from the trapping of stool small pieces in the appendix. Thus, creating an obstruction.
- There are also associations of lymph node swelling to appendicitis.
- Other associated condition with obstruction of the appendix is the gastrointestinal disorder called inflammatory bowel disease which involves ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
- The other less-likely associated factors related to appendicitis are stomach worms, fruit or vegetable seeds, and ingested barium for x-rays.
2. Infection
- Infection-related cause of appendicitis is linked to the bacterial growth that results from the trapping of feces in the appendix. As the bacteria multiply, swelling and pus fill up the appendix which just worsens the inflammation.
- Also, appendicitis is believed to be caused by gastrointestinal viral infection that may have travelled to the appendix. [1, 2, 4]

Picture 6: Causes of Appendix Pain
Source: emergencyus.wikispaces.com
Treatment for Pain in the Appendix
Surgery (Appendectomy)
Surgery is main and only treatment for inflammation of the appendix. Removal of the appendix is advised within the hours when diagnosis was made. This procedure is called Appendectomy. It is known to be a simple operation [2]. Appendectomy is performed under a general anesthetic, meaning the patient will be asleep during the entire operation [1]. Moreover, this can be performed through two methods:
1. Laparoscopy (Keyhole Operation)
- More commonly done because the recovery period post-surgery is faster compared to open appendectomy. Aside from this, this is typically performed because patients heal with minimal scarring.
- This involves making small incisions to allow the surgeon to remove the appendix. The incision is most likely 2 to 4 inches (5-10 cm) in length.
- During the operation, special surgical tools, including a video camera, will be inserted inside the abdomen.
2. Open appendectomy
- This is indicated when keyhole surgery cannot be done due to reasons such as ruptured appendix, presence of tumors in the digestive tract, pregnant women at their first trimester, and previous surgery of the stomach.
- In this case, the incision that will be made is a single large cut.
- This type of appendectomy also enables the surgeon to clean the abdominal cavity.
- Its disadvantages are larger scar and longer time for healing as well as hospital stay. [1, 4]
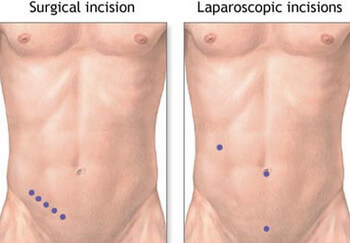
Picture 7: Incisions in Appendectomy
Source: pennmedicine.org
If the patient will not undergo appendectomy, it is more likely the inflamed appendix will perforate. This results to the occurrence of peritonitis, a medical condition which refers to the infection of the abdomen. When this happens, the patient may be faced with a life-threatening situation. [6]
Medications
- Anesthesia – General anesthesia will be given if the patient has no food and drink intake for the past six hours. However, if this is not the case, spinal anesthesia will be induced instead.
- Antibiotics
• Mainly administered to kill bacteria and decrease the likelihood of infection spread in the abdomen.
• Also, it is given to prevent the post-operative complications of the abdomen or the wound.
• Common examples are metronidazole and cefuroxime. - Pain medications
• May also be given prior to surgery
• During post-surgery, it is taken to relieve the patient’s pain and to aid in their mobilization. - Intravenous drip
• Started for the purpose of hydration - Anti-emetics
• Ordered if the patient is experiencing nausea or vomiting [5]
References:
- http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Appendicitis/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- http://bodyandhealth.canada.com/channel_condition_info_details.asp?disease_id=238&channel_id=9&relation_id=10860
- http://ministryhealth.org/ERMH/News/WhenIsaPainintheGutAppendicitis.nws
- http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/appendicitis/DS00274
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Appendicitis
- http://www.patient.co.uk/health/Appendicitis.htm
Published by Dr. Raj MD under Diseases and Conditions.
Article was last reviewed on August 6th, 2018.

