Leukopenia
What is Leukopenia?
Synonyms: leukopenia, agranulocytosis, leukocytopenia.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing defines leukopenia (pronounced: [loo″ko-pe´ne-ah]) as “any condition in which the number of leukocytes (white blood cells) in the circulating blood is lower than normal, the lower limit of which is generally regarded as 4000-5000 WBCs/mm3” [1].
Recent medical workups have shown that some health persons may register white bloods cells counts lower than 4000/mm3 with the opposite being also true. It has also been established that white bloods cells lower limits for infants/children varies with both age and sex.
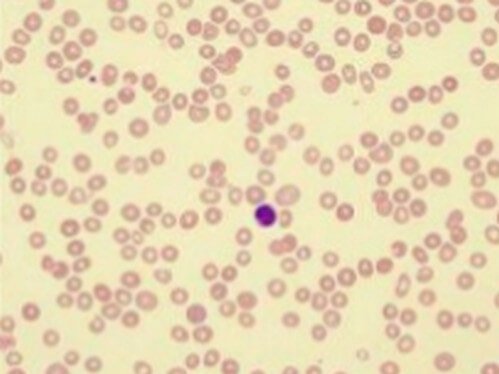
Leukopenia Smear
A person with leukopenia is at a higher risk of infection or invasion from opportunistic diseases because low white blood cells count has a direct implication on ones immune system.
Neutropenia is the most common type of leukopenia; use of the two words is sometimes swapped. It refers to a leukopenia type in which there is a decrease in the count of a specific type of white blood cells called neutrophils. Neutrophils, on its hand, form the most dominant type of white blood cells and are the primary defenders of the immune system. They are very effective in the defense against bacterial, fungal and viral infections. Other types of white blood cells include: basophils, monocytes, lymphocytes and eosinophils.
ICD-9 code for leukopenia is 288.5 [2,3,7,8,9]
Causes
“Pseudoleukopenia” is a false positive for leukopenia usually at the beginning of an infection such as from a septic wound. It is caused by a sudden migration of white bloods cells to the site of an infection. As a result, white blood cells count drops as the bone marrow begins to produce more. In reality, it is only detected as leukopenia when blood is tested just at the beginning of an infection. Thereafter, the white blood cells count would resume to normal as the bone marrow replaces the emigrant white blood cells.
Known causes are mainly medical conditions and medications.
Diseases or Medical conditions
There are several diseases and other medical conditions that cause leukopenia, most of which damage the key source of white blood cells (the bone marrow) or kill the white blood cells. In either case, white blood cells count drops depending on the extent of the damage. Some of the medical conditions that cause leukopenia are detailed below.
- Destruction or impaired functioning of the bone marrow: since bone marrow is responsible for production of white blood cells, any damage or suppression to it adversely affects white blood cells count hence leukopenia. Major causes of damage or impaired functioning of the bone marrow are as follows:
- Radio therapies: These include chemotherapy and radiotherapy which upon prolonged exposure lead to damage or suppression of the active sites of the bone marrow. As a result, there would be impaired production of white blood cells.
- Prolonged exposure to chemical agents and toxins like arsenic
- Attack from bone marrow cancers like Hodgin’s lymphoma or myeloma which targets and mutilates bone marrow cells.
- Myelodysplastic syndrome in which there is defective production of blood cells
- Myelofibrosis in which bone marrow tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue which hinders production of all types of blood cells [6,7]
- Diseases of the immune system – Diseases that affect the level/strength of the immune system such as HIV, AIDS, cold or influenza may cause severe viral infections that drastically reduce the number white blood in the body.
- Enlargement of the spleen: also known as hypersplenism. Since the key function of the spleen is to destroy white blood cells, its enlargement would fuel destruction of more white blood cells causing leukopenia
- Kostmann’s syndrome in which there is malfunctioned or limited production of white blood cells especially neutrophils
- Tuberculosis
- Myelokathexis in which there is impaired transfer of white blood cells into the blood.
- Vitamin and mineral deficiencies: important vitamins like vitamin B12 and minerals like folate are necessary for adequate production of white blood cells.
- Other diseases which may cause include: malaria, thyroid cancers, typhoid, anemia etc
Medications or drugs that cause Leukopenia
Patients under certain medication have experience leukopenia as a side effect. Mechanism of cause has been established to be aided by the immune system itself. White blood cells production is reduced when certain drugs are taken. Other drugs induce destruction of more white blood cells. Such drugs/medications include:
- Clozapine and carbamazepine: these are antipsychotic medications which have been established to hinder production of white blood cells as their side effects.
- Drugs which are used to treat epilepsy
- Immune system drugs
- Interferon drugs which are used in treatment of multiple sclerosis
- The antidepressant and smoking addiction treatment drugs have also been known to cause leukopenia if used for a long time
- Chemotherapy induces toxins which are destroys white blood cells causing leukopenia. [6,7]
Symptoms
The following are the symptoms that may likely show up when the number of white blood cells drops drastically:
- Inflammation of the gut mucous lining: such inflammation is a sign of wide spread infection which could lead to stomach ulcers or stomatitis.
- Prolonged and excessive menstruations are also a sign of leukopenia in that white blood cells cannot act timely to stop menstruation due to their dismal number. Excessive bleeding leads to further reduction in white blood cells.
- A person may also experience fatigue, high fever, headache and hot flashes
- A person with leukopenia is highly irritable
- Thrombocytopenia in which there is reduction in the level of platelets due to impaired functioning of the bone marrow.
- Anemia is also an indication of malfunction in the production of blood cells by the bone marrow. It is indicated by low level of hemoglobin or red blood cells.
- Pneumonia: pneumonia indicates wide spread infection in the lungs which may cause inflammation of lungs membrane. It is also an indication that the level of immune system has gone down due to reduction in the number of white blood cells.
- Infection of the liver: compromised immune system due to leukopenia may lead to an infection of the liver or liver abscesses
- Oral or tongue ulceration
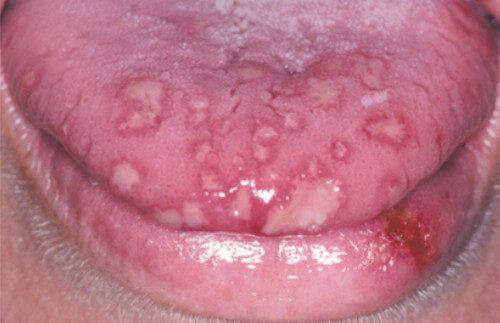
Oral Ulcer: http://pocketdentistry.com/
A person may get a strong urge to drink hot liquids [6,7,8,9]
Diagnosis of Leukopenia
As a rule of thumb, it is paramount to establish patient’s medical history when diagnosing for leukopenia and other related infections. It is important for the physician to know if the patient as causative diseases like diabetes insipidus or have undergone causative medical procedures like chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Otherwise, the following workup is required to establish white blood cells count:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) sometimes referred to as full-blood-count is carried out to establish white blood cells count. Ranges shown below provide reference values of various types of white blood cells [8]
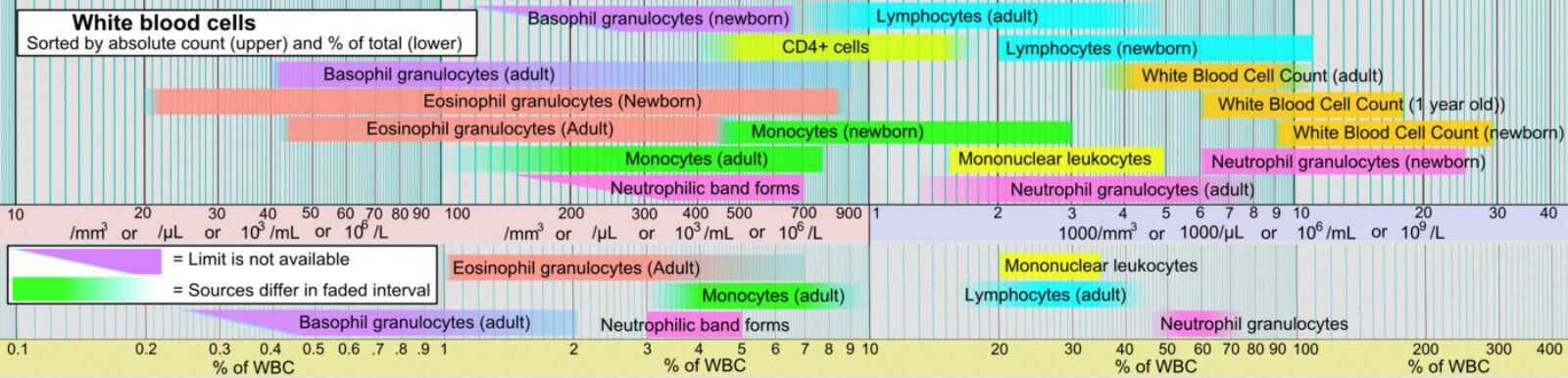
Figure CBC Reference ranges: DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.008.
- Scan of the bones to establish if there are any bone marrow defects.
- Platelet count: to check if there is any anomaly in the functioning of the bone marrow.
- Urinalysis: to check for presence of blood cells and infections in the urine
- Serum protein electrophoresis: to test for plasma proteins levels
- Vitamin and mineral deficiency tests: this is done to check for any deficiency especially in B12 and foliates
- CT scan to check the health of both liver and spleen
- Check for Hodgkin’s lymphoma and myeloma through a lymph-node biopsy
Leukemia Workup
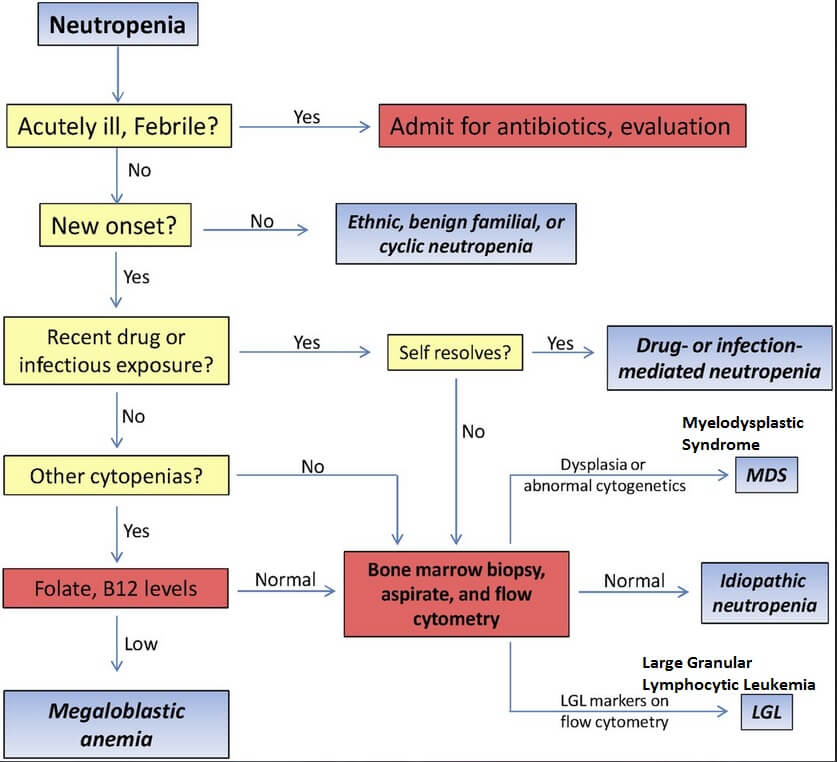
Treatment and Management
Treatment of leukopenia is usually cause-specific; it targets the root cause of leukopenia rather than leukopenia itself. High hygiene is paramount in preventing infections which cause leukopenia. It is generally treated or managed through the following ways:
- Certain vitamins and steroids can be used to induce normal functioning of the bone marrow. They are administered to activate sites that produce white blood cells in the bone marrow.
- A doctor may advise a leukopenia patient to do away with medication that induce leukopenia or provide harmless alternatives.
- Some doctors advise their patients to get proper sleep for the immune system to regroup.
- Anti-cancer medications and therapies such chemotherapy may be prescribed to patients with lymphomas or myeloma to resuscitate production of white blood cells
- Antibacterial drugs or other antibiotics may be administered to deal with infections that deplete the body of white blood cells
- Vitamin and supplements to aid weakened immune system
- In the case of severe case of leukopenia, a doctor may prescribe cocktail of drugs that target both the causative agents and leukopenia itself. [7,8,9]
References;
- TheFreeDictionary.com. leukopenia [Internet]. 2015 [cited 14 December 2015]. Available from: http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/leukopenia
- Mayoclinic.org. Low white blood cell count – Mayo Clinic [Internet]. 2015 [cited 14 December 2015]. Available from: http://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/low-white-blood-cell-count/basics/definition/sym-20050615
- Icd9data.com. 2012 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 288.50 : Leukocytopenia, unspecified [Internet]. 2015 [cited 14 December 2015]. Available from: http://www.icd9data.com/2012/Volume1/280-289/288/288.50.htm
- Siamak N. Nabili M. Thrombocytopenia (Low Platelet Count) Causes, Symptoms, Treatment – Thrombocytopenia Causes – eMedicineHealth [Internet]. eMedicineHealth. 2015 [cited 14 December 2015]. Available from: http://www.emedicinehealth.com/thrombocytopenia_low_platelet_count/page2_em.htm
- WebMD. Neutropenia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment [Internet]. 2015 [cited 14 December 2015]. Available from: http://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/neutropenia-causes-symptoms-treatment
- Md-health.com. Leukopenia | MD-Health.com [Internet]. 2015 [cited 14 December 2015]. Available from: http://www.md-health.com/Leukopenia.html
- Wikipedia. Myelodysplastic syndrome [Internet]. 2015 [cited 14 December 2015]. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Myelodysplastic_syndrome
- Wikipedia. Leukopenia [Internet]. 2015 [cited 14 December 2015]. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leukopenia
- Ing V. The Etiology and Management of Leukopenia. Canadian Family Physician [Internet]. 1984 [cited 14 December 2015];30:1835. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2154209/
Published by Dr. Raj MD under Diseases and Conditions.
Article was last reviewed on August 6th, 2018.

