Nodular Melanoma
The most important topic regarding nodular melanoma is early detection. This is repeated in every study and article published regarding this topic.
If you have familiar tendencies toward skin cancer or have many skin lesions please consult your doctor regarding nodular melanoma. Be aware of the causes and how to prevent skin cancer. If skin cancer is detected it is suggested to join a medical study because there is still much to learn about prevention, causes and treatment of nodular melanoma.
What is Nodular Melanoma? In this section you will better understand what nodular melanoma is and some common known facts regarding this diagnosis.
- According to the article Dermoscopic Evaluation of Nodular Melanoma,
- Nodular melanoma (NM) is defined as an invasive melanoma which lacks significant intraepidermal tumor cells beyond the margins of dermal invasive component. (1)
- According to Wallace Clark and colleagues histopathological classification which is accepted by the World
- Health Organization nodular melanoma is one of four subtypes of melanoma. (4) (Nodular melanoma, Acral lentiginous melanoma, Lentigo malignant, Superficial)
- Any cancer involves abnormal cell change.
- It is one of the most common cancers detected. (8)
Nodular Melanoma Diagnosis
In this section you will better understand how to recognize nodular melanoma and how your doctor can make an educated decision on your diagnosis.
- ABCDE Rule- raises consciousness about skin lesions. The earlier nodular melanoma is detected the better the prognosis (1–12)
- Asymmetry
- Border irregularity
- Color
- Diameter (larger than a pencil eraser) (4,8)
- Eloving
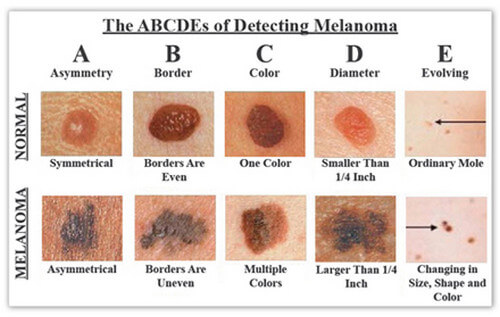 Picture 1: The ABCDEs of Detecting Melanoma
Picture 1: The ABCDEs of Detecting Melanoma
Image Source: foot-pain-explained.com
- At times nodular melanoma fails to be detected with the mentioned ABCDE rule.(1,4)
- Any time a skin lesion has progressive growth nodular melanoma should be discussed. (1,4)
Pictures
Nodular Melanoma Symptoms
Listed below are the most common symptoms. But as stated in most all studies and articles regarding nodular diagnosis this list is far from complete. Be sure to have any changes in skin lesions checked by your doctor.
- Changes in size, color, texture, shape.
- Wounds that will not heal. (8)
- Changes in existing moles as an adult
- Dark or back spots which may appear in existing moles.
- Shiny, firm, dark bumps
- Any type of skin lesions larger than a pencil eraser. (11)
- Is more common on the extremities, chest of back. It can also appear on the palm of the hand, sole of the foot, and under fingernails or toenails. Less commonly it can be seen in the mouth, vagina, anus or the eye. (8)
- Usually invasive, ulcerated and have mitoses (4)
Treatment choices for Nodular Melanoma
This is a list of the most common treatments but it is not extensive and if your doctor suggests other treatments remember to follow their recommendations.
- Surgical treatment and removal of the lesion is the most common response to nodular melanoma. (1–12)
- Chemotherapy may be added to surgery depending on the stage of diagnosis.
- Immunotherapy is needed when and if Chemotherapy has been prescribed.
- Inhibitor target therapy includes prevention of cancer cell growth or metastasis.
- Medications that may be injected directly into the tumor.
- Lasers may be used to destroy and remove the tumor.
- If the melanoma metastasizes treatment of the metastatic melanoma is the same as noted above.
- If recurrent melanoma or a relapse is noted then all the above stated treatments are the same.
- Regular follow up appointments are necessary. (12)
- Early detection is necessary (1–12)
Prevention
- Decrease skin exposure to the sun. (1,11)
- Frequent self-skin exams
- If suspicious lesions arise check with your physician to see if a skin biopsy is necessary.
Checking of lymph nodes. - Imaging testing may be prescribed if suspicious lesions are noted. Including but not limited to PET scan, CT scan, and MRI (11)
Nodular Melanoma Survival Rates/Prognosis:
As stated many times in this article and many others early detection is the key.
- Nodular melanoma is a frequent subtype of thick, rapidly growing melanoma.
- Frequently not diagnosed in time to increase a positive prognosis. (1)
- If caught early and treated has a very positive prognosis (1–12)
- Prognosis depends largely on the thickness of the primary lesion (2)
- Early detection and treatment can prevent relapses. (2)
Nodular Melanoma Stories
As noted in the Case report of nodular melanoma within congenital melanocytic nevus- primary closure challenge a 72 yrs male with a chronic history of alcohol dependence who developed liver cirrhosis and has a history of pacemaker placement. He was born with lesion present in the mid-line of posterior trunk area. During his lifetime he couldn’t attend regular checkups.
He noticed a nodule and was advised for surgical excision of the lesion and final pathological examination confirmed that it was nodular type of melanoma with ulceration.
He Was later planned for reexcision from the previous surgery with margins (2 cms) and also SLNB in inguinal region (each). Due to the possibility of satellites and patient’s wishes a total removal was planned. It was decided to perform a triple Limberg flap and versatile local flap (5).
As stated in the Nodular Melanoma Serendipitously Detected by Airport Full Body Scanners, a 50-year-old businessman who traveled at least twice per week throughout the USA via airplane for his job.
After years of traveling without incident, the airport full body scanner suddenly singled out an area on his left lower leg for a pat-down. With only one or two exceptions, this continued to happen during every trip (20 flights) for the next 2 months. The patient had no prior surgeries or implants in this area (6)
References:
- http://archderm.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=1675049 Dermoscopic Evaluation of Nodular Melanoma
- Tumori, 97: 35-38, 2011 Small nodular melanoma: the beginning of a lifethreatening lesion. A clinical study on 11 cases
- http://archderm.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=419298January 1, 2008, Vol 144, No. 1 Primary Dermal MelanomaDistinct Immunohistochemical Findings and Clinical Outcome Compared With Nodular and Metastatic Melanoma
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3253944/ superficial spreading and nodular melanoma are distinct biological entities: a challenge to the linear progression model
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4818315/Case report of nodular melanoma within congenital melanocytic nevus- primary closure challenge
- http://www.karger.com/Article/Pdf/368045
- http://www.jidonline.org/article/S0022-202X(15)32417-9/pdf
- http://www.webmd.com/melanoma-skin-cancer/melanoma-guide/understanding-skin-cancer-basics
- http://www.webmd.com/melanoma-skin-cancer/melanoma-guide/skin-cancer-melanoma-what-happens
- http://www.webmd.com/melanoma-skin-cancer/melanoma-guide/sunburn-and-skin-cancer-topic-overview
- http://www.webmd.com
- http://www.webmd.com/melanoma-skin-cancer/melanoma-guide/skin-cancer-melanoma-treatment-overview
