Most of us are aware of the medical term, ‘fracture’. It means breakage of bones. Fractures are caused when the tensile strength of the bone is overcome by the deforming forces acting on the bones.
There are different types of fracture based on the bone in which it occur and the mechanism by which it is caused.
One such unique type of fracture is the greenstick fracture. [1]
What Is a Greenstick Fracture?
To understand a greenstick fracture, you should recall, how a young green stick breaks when you snap it.
It bends initially and then it breaks. In the same way, when the bone is young, it is soft and pliable like a green stick. When there is an impact on such a bone, it bends and then breaks rather than completely breaking into fragments as is the case in other types of fractures. Such a fracture is called greenstick fracture.


Fig 1: Greenstick fracture
Image source – 1: socialballroom.dance
Image source – 2: s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.com
It is an incomplete fracture in which there is a transverse fracture line causing disruption of the outer layer of a bone (cortex), extending onto the core or medulla of the bone without disrupting the opposite cortex. Thus the discontinuity is on one side only. [2]
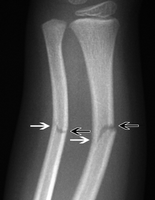
Picture 2. X Ray – Greenstick fracture
Image source – blogspot.com
It is a childhood fracture commonly occurring in children younger than 10 years of age due to the softness and flexibility. But it is not exclusive to childhood. Cases have been reported in adults commonly involving the forearm. Thus the morphology of the bone is the main factor resulting in greenstick fracture.
Causes Of Greenstick Fracture
The causes of greenstick fracture are similar to that of other types of fractures i.e forceful impact to the bones such as fall, blow or twisting force. As young children love to play outdoors and involve in physical activities, they are more prone to injuries. Although any type of force can result in fractures, fall from height is the common cause among children. They engage in jumping activities which may result in frequent falls.
Symptoms
Like other types of fracture, the chief complaint of greenstick fracture is also pain. Intense pain at the site of injured area of child should raise suspicion. When the greenstick fracture is mild, it appears like a simple bruise with swelling, redness and warmth.
When the greenstick fracture is severe, there may be obvious deformity of the limb. Greenstick fractures are more commonly in upper limb than lower limb. As the greenstick fracture may not present with the severe swelling and deformity of other types of fracture, it is necessary to take precautions to rule out greenstick fracture when the child doesn’t come forward with a proper explanation of the injury. [3]
Greenstick Fracture Of Clavicle
Fracture of clavicle happens during fall with outstretched hand or direct blow to the upper chest and shoulder. Clavicle becomes hard and fully matured only after 20 years of age. Thus greenstick fracture in clavicle is possible even in adolescence.
Greenstick Fracture Of Wrist
Greenstick fracture of wrist is actually the fracture in the lower third or middle third of radius or ulna (the bones in forearm). This happens when a child falls flat on the floor with outstretched arm or impact to the palm while falling from height. Direct blow to the forearm may result in the greenstick fracture of upper and middle third of radius or ulna. [4,5]
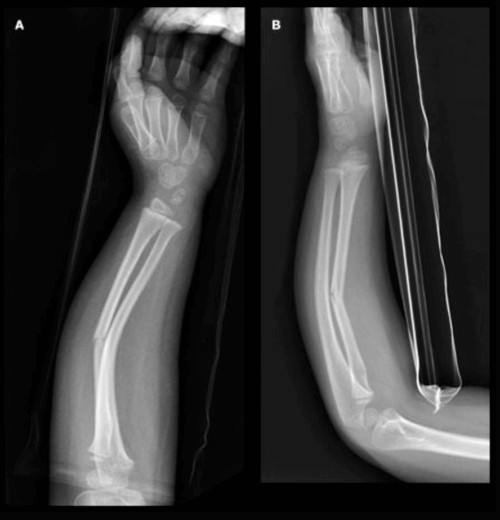
Fig 4: Greenstick fracture radius and ulna
Image source : cursoenarm.net
Greenstick Fracture Of Tibia
Greenstick fracture in tibia occurs while landing on foot in fall from height or due to blow to leg. But the force required for causing fracture to the tibia is higher than the force causing fracture in radius and ulna. The common sites of fracture are middle third and lower third of shaft of tibia.
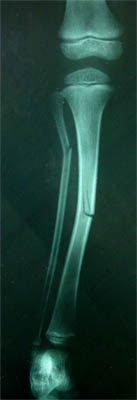
Fig 5: Greenstick fracture of tibia and fibula
Image source – voyager.dvc.edu
Greenstick Fracture Treatment
The severity of the greenstick fracture is assessed by X-Ray of the affected limb and then it is treated accordingly. The mainstay of the treatment is to bring the bones to their original position and to allow them to unite in their natural position. This is done by immobilising the limb to prevent undue pressure on the fractured limb. [6,7]
If there is deformity of the affected limb, the bones are aligned properly by manipulation which is usually done under pain relieving medications or sedatives. Thus, when the manipulation is done properly, it is a painless procedure. The affected limb is then immobilised in a plaster cast or a splint.
The removable splints are comfortable for children than the casts. Repeat X-Rays are taken after few weeks to assess the healing of the fracture. When the bones have united properly, the cast is removed.
Image source – healthtap.com
The healing time of greenstick fracture depend on the severity of the fracture, the bone involved, the age and general health of the child. Usually, the greenstick fracture may completely heal in 30 – 60 days.
Thus greenstick fracture is nothing to be feared of. It is necessary to diagnose the fracture in the timely manner and immobilise the limb for the stipulated time. As the bones of children are in their growing phase, the greenstick fracture heals well without any deformity with proper medical care.
Picture source – joint-pain-expert.net
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greenstick_fracture
- https://www.drugs.com/cg/foot-fracture-in-children.html
- Diagnosis and treatment of greenstick and torus fractures of the distal radius in children: a prospective randomised single blind study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2908342/ - http://www.radiologymasterclass.co.uk/gallery/trauma/x-ray_arm_1/fractures_11
- Greenstick fractures of the radius in adults: a report of two cases
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8667114 - http://www.childrensortho.com/our-services/trauma/stress-fracture-of-the-foot/
- Greenstick fracture of the mandible: A case report http://www.jisppd.com/article.asp?issn=0970-4388;year=2008;volume=26;issue=1;spage=32;epage=35;aulast=Kalia
