Precordial Catch Syndrome
It is not uncommon to see a kid complaining of chest pain in one of the days.
Usually it is misread by the parents or the caretakers as the child faking it to avoid school or as an acid reflux. Some parents get scared thinking that something is seriously wrong with the child’s heart. In both cases they are wrong and they don’t know that it may be caused by a common harmless condition called Precordial Catch syndrome [PCS].
What is Precordial Catch Syndrome?
Precordial catch syndrome is a common and misdiagnosed condition causing a sharp chest pain in the left side which is always benign. It is also known as Texidor’s twinge after Texidor and Miller who described it for the first time in 1955. [1, 3, 5]
Who gets Precordial Catch Syndrome?
Precordial Catch syndrome can occur in any age, but most commonly affects children of age group 6-12 years. Men and women are equally affected and it is less commonly seen in adults [1, 5]
Causes
What causes Precordial catch syndrome and how it is caused is still a mystery. Texidor and Miller thought that it may be due to involvement of the pleura which is the layer of tissue covering the lungs. Later on clinicians believed that it may be caused by muscle cramp that occurs in the group of muscles that are present between each ribs in anterior chest region (the intercostals muscles) [1]. Some researchers suggest that it may be a pinch on a nerve. Whatsoever, there are no proven causes for PCS. Yet, researchers have found some aspects aspects that might trigger Precordial Catch syndrome in children. They are [4] [1, 5, 6]
Costochondritis
It is the inflammation of the joint between sternum and the ribs. In children it is caused by viruses causing respiratory disease. Hence it is associated with coughing
Injuries
Injuries that damage the muscles in the chest may cause PCS
Stress and anxiety
Though stress and anxiety is rare among children, it is one of the aspect causing the muscle cramps in the intercostals muscles causing PCS [3]
Unhealthy food
Unhealthy and inappropriate amount of food is also an aspect causing PCS in children
Respiratory diseases
Children with lung disease have difficulty in breathing. They sometimes present with PCS
Symptoms of Precordial catch Syndrome
The most important and only symptom of Precordial catch syndrome is chest pain [1, 2, 5]
Characteristic of the chest pain
- Sudden to appear
- located in the chest, a little away from the sternum towards left, where the cartilages are present
- Pain varies in intensity from dull discomforting pain to Sharp pain like plunging a needle or knife. Pain increases on taking a breath or moving.
- The pain stays where it has started and does not radiate anywhere which is the case in most cases of heart attack
- The pain lasts from few seconds to few minutes and goes off by itself without need for any medications. Sometimes the pain lasts for around 30 minutes. Some people get the pain many times a day while some get it less frequently. It has individual variations.
- The pain never occurs in sleep
- People may volunteer slow down their breathing and stop moving.
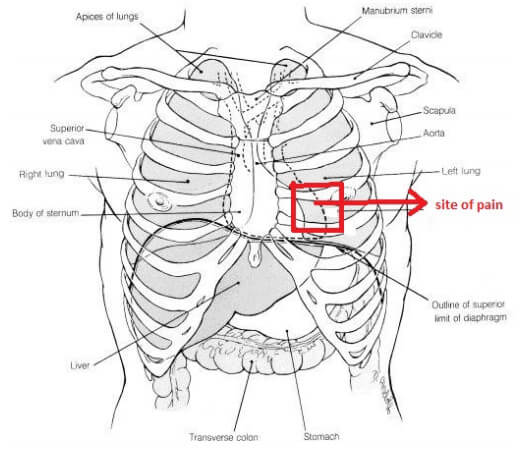
Picture 2: Site of pain in Precordial catch syndrome
It is essential to differentiate Precordial catch syndrome from life threatening conditions like heart attack and pulmonary embolism for which chest pain is the most important presenting symptom. These life threatening conditions can be treated if they are diagnosed immediately.
Heart attack or Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction literally means death of the heart muscle. It is caused by poor blood supply or almost no blood supply to a part of heart muscle which then die. It presents with a sharp pain over the left side of chest which develops suddenly and does not get relieved on taking rest. It is associated with a group of symptoms like excessive sweating, fainting, nausea, vomiting and a chocking sensation : [9, 10, 11]
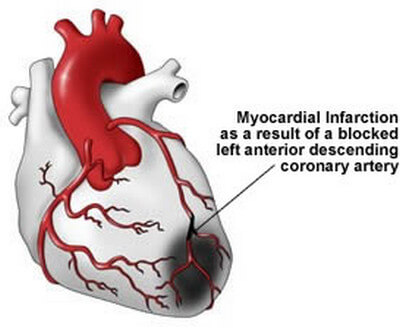
Picture 3: myocardial infarction caused by heart muscle death
Image Source: pyroenergen.com
Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism is a condition in which there is a blood clot that moves freely in the blood stream and has blocked one of the blood vessels carrying blood from the heart to the lungs. It presents with sudden breathlessness, chest pain that worsens on breathing, coughing up of blood [7, 8]
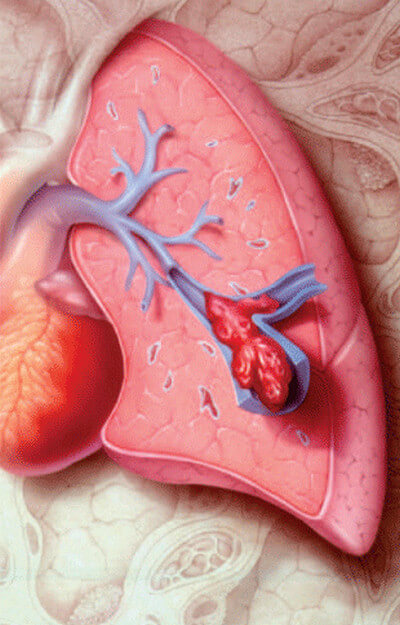
Picture 4: Pulmonary embolism
Difference between PCS and Heart attack
| Precordial catch syndrome | Heart attack |
|---|---|
| Pain is localized. Not radiating | Pain radiates to left shoulder, arm and jaw |
| The site of pain can be pointed out with tip of a finger | The site of pain is pointed with a clenched fist. |
| Pain gets relieved in few minutes | Severe pain persists |
| Not associated with other symptoms | Associated with excessive sweating, giddiness and nausea |
| Normal ECG | Typical changes in ECG |
Difference between PCS and Pulmonary Embolism
| Precordial catch syndrome | Heart attack |
|---|---|
| Pain is localized. Not radiating | Pain radiates to left shoulder, arm and jaw |
| The site of pain can be pointed out with tip of a finger | The site of pain is pointed with a clenched fist. |
| Pain gets relieved in few minutes | Severe pain persists |
| Not associated with other symptoms | Associated with excessive sweating, giddiness and nausea |
| Normal ECG | Typical changes in ECG |
Diagnosis of Precordial catch syndrome
A careful history taking and physical examination is needed to rule out other serious causes of sudden chest pain and to diagnose PCS. The following tests are normal in case of Precordial catch syndrome.
To rule out heart diseases
- Electrocardiogram and Echocardiogram
To rule out lung involvement and bone diseases
- Chest radiograph – plain
Rule out occult diseases in rib
- Radionuclide bone scan in people with history of injury to
To rule out joint instability between sternum and ribs
- Scans like MRI
To rule out inflammatory and infectious conditions
- Blood investigations – Total blood count, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate etc
Treatment of Precordial catch Syndrome
- No treatment is needed and there is no cure available.[1,3]
- Other than the brief spell of sharp pain, the only effect of this condition is the panic and anxiety to the patient
- The children and their anxious parents should be reassured that it is a medically benign condition and it doesn’t need any medication or procedures [2]. One should familiarize the patient and their family about the condition and explain it to them in such a way that they need not panic unnecessarily and they should not overlook any other condition causing chest pain as PCS
- While the people are scared to take a breath during the episode, the pain actually gets relieved on taking a deep breath when the pain starts.[2,5]
- A change of position like sitting up from slouching and massaging of the chest may relieve pain
- Eating healthy food in appropriate amount and having a physically active lifestyle may help [4]
Prognosis
It is a discomfort and not a life threatening or dangerous condition. It needs no medication or treatment. It usually resolves in adulthood and does not have any bad effect on health. [3]
Differential Diagnosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Myocardial infarction or heart attack
- Pericarditis
- Costochondritis
- Pleuritis
- Chest injuries like rib fractures [1, 5]
Even though Precordial catch syndrome is a harmless condition, one has to get a clinician’s opinion to confirm the diagnosis so that there is no necessity to panic when the next episode sets in.
References
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Precordial_catch_syndrome
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1627421/pdf/archdisch00769-0087.pdf
- http://www.precordialcatchsyndrome.org/causes-symptoms-and-treatments-for-precordial-pain/
- http://www.precordialcatchsyndrome.org/the-aspects-that-lead-to-precordial-catch-syndrome-in-children/
- http://www.physio-pedia.com/Precordial_Catch_Syndrome
- http://syndromespedia.com/precordial-catch-syndrome-treatment-symptoms-causes.html
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pulmonary_embolism
- http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-embolism/basics/definition/con-20022849
- http://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/understanding-heart-attack-basics
- http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/155919-overview
Published by Dr. Raj MD under Diseases and Conditions.
Article was last reviewed on August 6th, 2018.

